A Brief History of Computers

A Brief History of Computers
August 7, 2023
While the younger generations were born surrounded by technology and might not even remember life without modern computers, some still reminisce about the colossal, outdated computers that first revolutionized the world.
Little by little, computers became an integral part of our lives, transforming the way we work, communicate, and access information. But have you ever wondered how these incredible machines came into existence?
From humble beginnings to the sophisticated devices we use today, let’s embark on a journey through time to explore the fascinating evolution of computers.
The Birth of Calculating Machines
The word “computer” comes from the verb “to compute”, which means “to calculate”. Contrary to what you might think, the origin of computers can be traced back to ancient civilizations with the sole aim of helping in calculation!
Although it’s difficult to pinpoint its exact time and place of origin, the abacus is believed to have been invented between 2,700 BC and 300 BC. The early computing tool consisted of beads or stones placed on rods, enabling basic arithmetic calculations.

Yes, the first computer looked like this!
It wasn’t until the 17th century that we saw advancements in mechanical calculating devices with the invention of the first automated calculated machine by the French mathematician Pascal.
Already in the 19th century, visionary mathematician Charles Babbage conceptualized an Analytical Engine, a mechanical computer capable of executing complex instructions. Roughly speaking, the machine is compared to modern computers with memory and programs – the reason why he is considered the “Father of Computing”.
The Path to The Electronic Era
The computer, as we know it today, has undergone several transformations, following advances in the fields of mathematics, engineering, and electronics. That’s why there is not just one inventor. The true revolution in computing began in the mid-20th century with the advent of electronic computers and it can be mainly divided into five periods:
First Generation (1940s-1950s): The Valves Era
First-generation computers worked by means of electronic circuits and valves. Z3, the world’s first programmable electromechanical computer, was created by Konrad Zuze in 1941 and paved the way for future innovations.
Yet, the ENIAC (Electronic Numerical Integrator and Computer) was the one considered the first general-purpose electronic computer. Created in 1946, the ENIAC marked a turning point by enabling faster and more flexible computations.
Besides being massive machines, these computers were very unreliable since they would frequently heat up and shut down. They also had very restricted use and consumed a lot of energy. The ENIAC, for once, consumed around 200 kilowatts and had 19,000 valves!
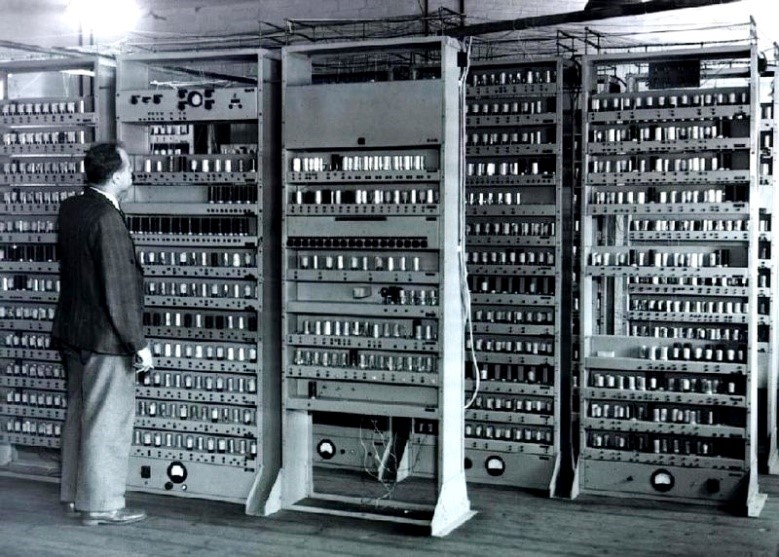
Second Generation (1950s-1960s): The Discovery of Transistors
The invention of the transistor in 1947 revolutionized computing technology, opening doors for the second generation of computers. The first computer to ever use transistors was the UNIVAC (Universal Automatic Computer), created in 1951 by the engineers responsible for the ENIAC – a turning point in the history of computing.
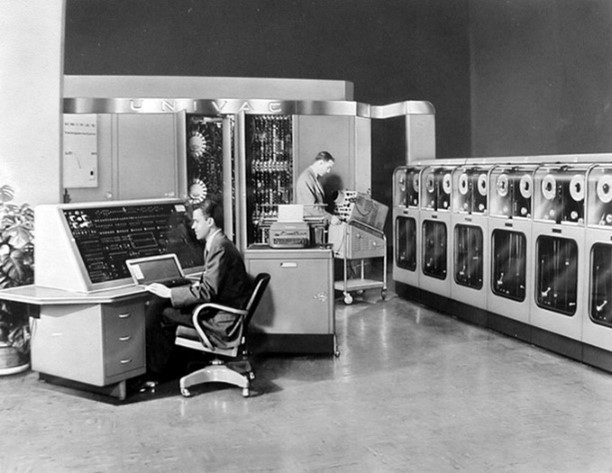

Replacing bulky and unreliable vacuum tubes with transistors was a monumental leap in computing technology. Although they still had very large dimensions, the computers of the second generation were smaller, faster, more reliable, and consumed less power. In this period, they also began to spread in commercial use.
Third Generation (1960s-1970s): The Advent of Integrated Circuits
The third generation of computers introduced the use of IC (integrated circuits) in computers, which helped reduce their size and made them faster. Half a century later, computers still have deep roots going back to the third generation, with ICs still being currently used in computers!
One of the first computers to use integrated circuits was the IBM/360, launched in 1964. Very advanced for the time, it made other computers look totally obsolete, causing IBM to sell more than 30,000 computers. The IBM/360 computer is considered by many one of the most successful in computer history, influencing the design of new machines for years to come.
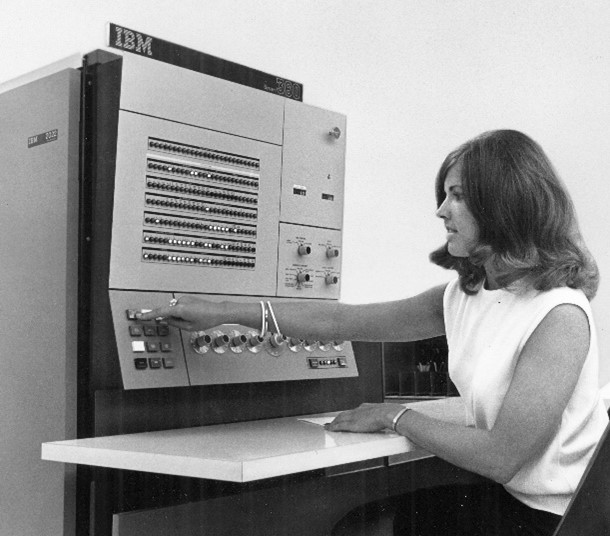

Fourth Generation (1970s-1980s): The Personal Computer Revolution
The fourth-generation computers were developed by using microprocessor technology, which significantly lowered energy consumption. This generation had the first “supercomputers”: computers decreased in size and increased speed and data processing capacity.
The 1970s witnessed the birth of the personal computer (PC), which brought computing power directly to individuals. Companies like Apple and IBM played main characters in popularizing PCs, making them accessible to a wider audience. These computers were much more reliable and consumed far less energy in comparison to the previous generations.
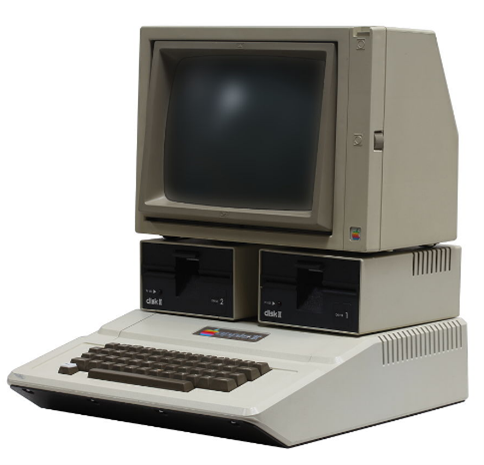

The original PC (Personal Computer) was actually created by IBM in 1981! The IBM 5150 was launched as an attempt to enter the home computer market, dominated by Apple Inc since the release of the Apple II computer in 1977.
Fifth Generation (1980s-present day): The Internet and Beyond
Thanks to the creation of the World Wide Web in 1989, the 1990s marked the rise of the Internet, connecting computers worldwide and paving the way for the digital age we live in today.
Advances in computer technology continued to accelerate and from the 90s onwards, there was a great expansion of personal computers. The machines of the fifth generation had high capability and large memory capacity, they were faster, and they could perform multiple tasks simultaneously.
From the turn of the millennium, handheld computers began to appear, such as laptops and tablets. The Osborne 1 was launched in 1981 and it’s considered the first true mobile computer. In 1989, it was time for the first commercially successful tablet computer to appear – GRiDPad 1900.

Today, we are familiar with the most modern computers and laptops, and they became an essential tool in our lives, not only at home but at work. Although Apple is still a beloved computer option by many, in recent years, Lenovo has been the global market leader in computers since 2013 (apart from 2017)!
Sixth Generation: What The Future Holds
Although we are still living in the fifth generation of computers, we are beginning to see promising technologies, such as Artificial Intelligence (AI), representing a new era of technological prowess.
One of the most remarkable features of the sixth generation is the widespread implementation of Quantum Computing, enabling computations at unimaginable speeds and solving complex problems previously deemed impossible.
With a new generation of computers, it’s also possible that the way we interact with computers may also change. The sixth generation is characterized by seamless integration with the Internet of Things (IoT), leading to a highly interconnected world with smart devices enhancing daily life in ways we could have only dreamed of in the past.
Did you know…?
Computer Science Day is celebrated on 15th February, the date that marks the appearance of the first electronic digital computer, ENIAC!